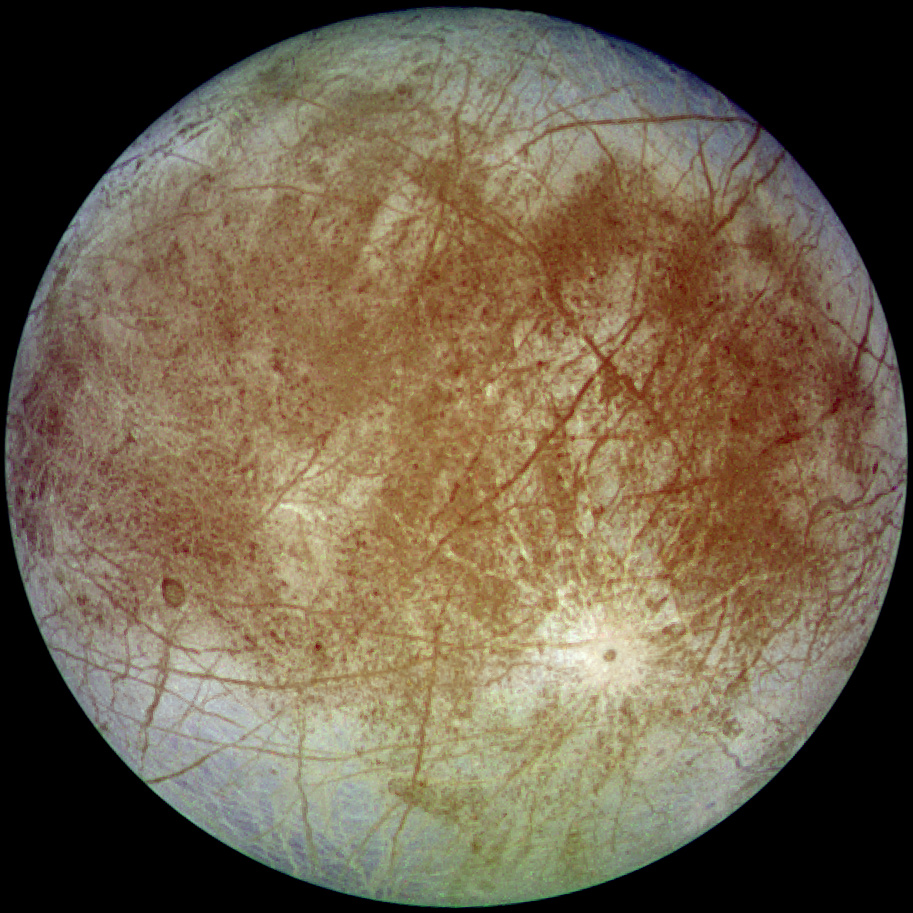
For thousands of years, humans have considered the possibility of life existing on other planets – specifically those in our own solar system. Perhaps one of the most prime candidates for harboring life in our Solar System (other than our own planet, of course) is Europa – one of Jupiter’s 4 largest moons.
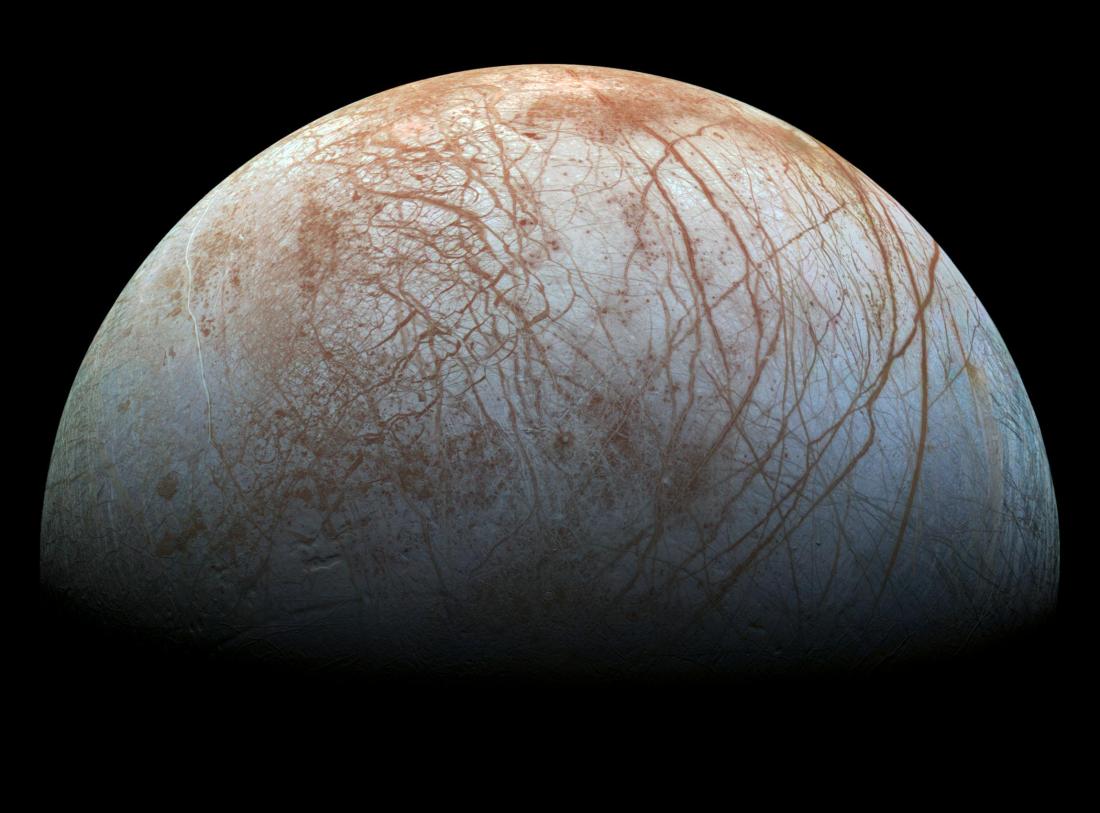
Europa, the ice-covered moon of Jupiter, has all of the necessary conditions for life- liquid water (under the ice-covered surface), organic compounds, and energy. In addition to this, its reddish-brown surface color has piqued the interest of NASA scientists, who speculate that this color comes from microorganisms frozen in the ice. To test this hypothesis, NASA scientist Brad Dalton, simulated Europa’s conditions (-162 degrees Celsius, at 10-7bars of pressure) and measured the infrared signatures of 3 different types of bacteria – Escherichia coli (E. coli), Deinococcus radiodurans, and Sulfolobus shibatae. He then compared these signatures to those collected by the Galileo spacecraft and found that they are strikingly similar to each other, with the exception of two spectral lines present in Dalton’s bacteria that weren’t present in the data collected by Galileo. He argues, however, this can be attributed to the radiation on Europa’s surface disintegrating layers off of the bacteria that are responsible for the spectral lines. As exciting this prospect of life is, this evidence is by no means concrete (and we may never have definite answers until we physically visit Europa ourselves) – but until then we must continue collecting evidence that support (or disprove) the theory of life on Europa. As Dalton says “More work is needed to be done”.